US presidential elections 2016 - analysis with facebook scrapper and elastic-search
[scrapping elasticsearch facebook 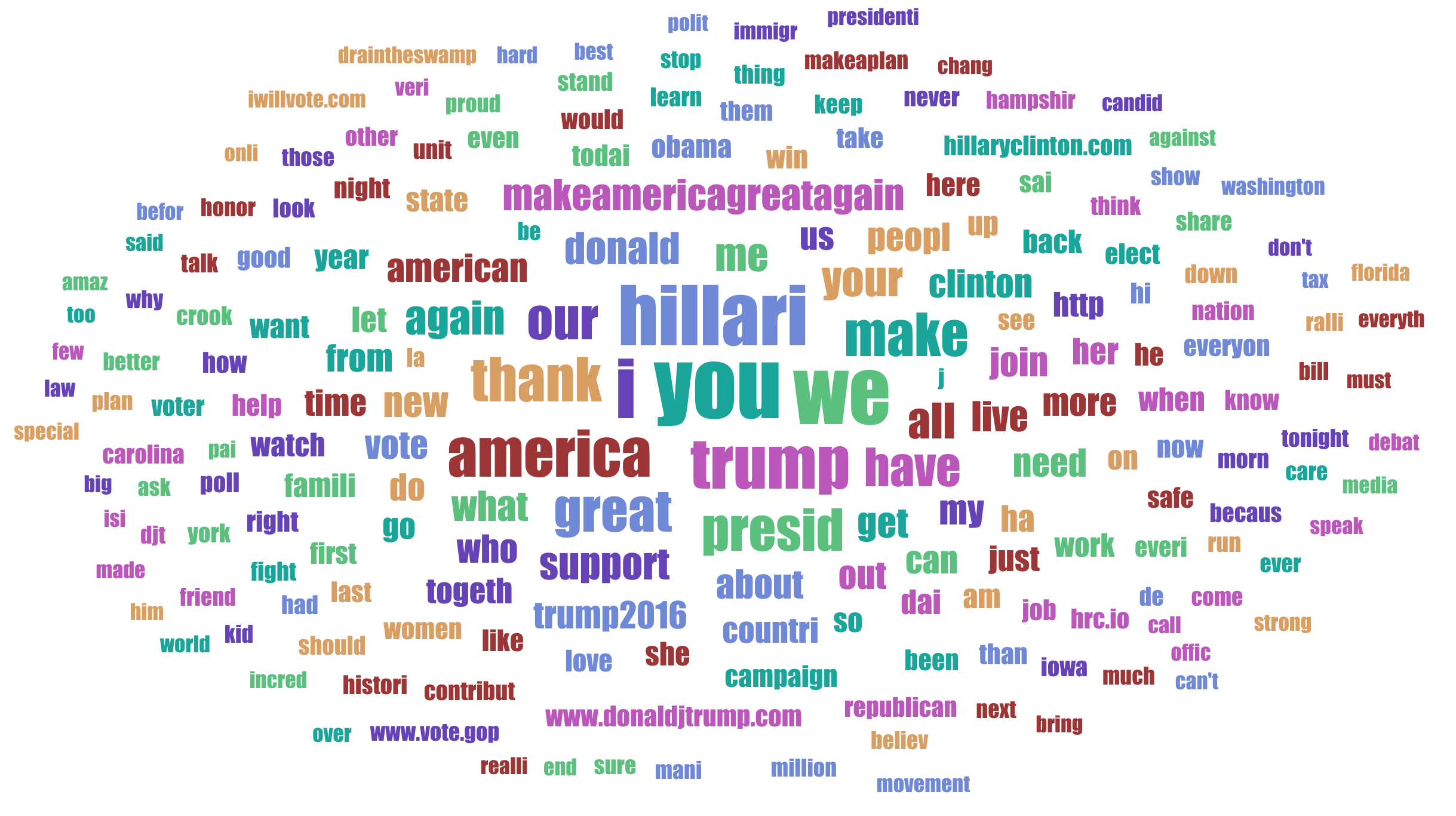
Problem Statement
The year 2016 was one of the most talked about years in the 21st century about elections in the United States with the main reason being for the first time the elections included a presidential candidate who never had a political background and is one of the most disctinct personalities in America. Yes, It is Donald Trump that we are looking at.
With all the issues, controversial videos leaked, media pressure on Donald Trump taking everyone by surprise, Trump became the president of the United States of America defeating an extremely famous politician by the name Hillary Clinton. I decided to find out the insights on what really made Donald the favourite among the American people.
The presidential elections also had its share of the digital machines a.k.a computer influencing the people of America. A few noteworthy incidents that occured then:
- russian ads targeting specific groups of people
- cyber attack and email leaks
- facebook bots abusing the graph API, posting comments on most public posts by senators of both parties
- twitter bots constantly re-tweeting their favourite tweets by their nominees
[*] To some extent bots expressed their views more on the presidential candidates compared to humans
As there were so many bots involved in posting comments and replying to comments, we will focus on only the posts made by Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton themselves for this exercise. So our problem statement for this activity will be
What ideas were installed in the minds of the american people through social media posts by the presidential candidates Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton ??
Requisites
For this activity we need some basic working skills in the following language/frameworks.
In case you are not familiar with Elastic Search or Kibana you can get this super cool udemy course by Frank Kane on elastic search. I took this course last month and I have to admit Frank is one of the best teachers for Elastic Search right now.
Let’s start writing our simple script
Facebook needs no explanation for what it is. But the Graph API of facebook needs an explanation.
"Graph API of facebook lets you scrap and download any public available data that's been written(posts)/stored(images)/performed(check-ins) in facebook"
Run a scrapper program for a few hours for your favourite celebrity page e.g. Ed Sheeran (in my case) and you can get all that he’s posted, all the comments made on his posts, all the photos that he’s posted and all feeds that he’s mentioned. Crazy isn’t it
So I started with getting all the posts of the most loved and equally hated Donald Trump posted between the time frame 8-Nov-2015 and 8-Nov-2016 which is the presidential election date. I did the same with Hillary Clinton as well.
I used a very simple and straightforward python script to achieve this. Let’s dive right in.
Import the modules that we are going to be using in the scrapper program
import facebook
import requests
import jsonJust in case you are wondering what is import facebook means , facebook-sdk is the python wrapper for the graph API. To access the graph API you would need an access token which can be obtained by clicking on this link. You would need a fb account to get the token.
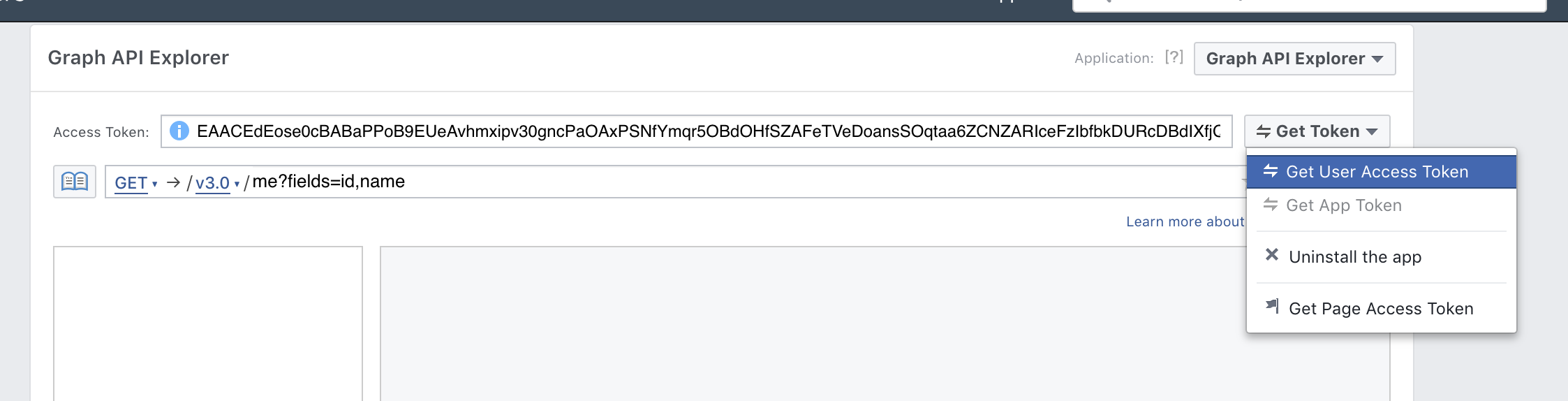
Click on the Get User Access Token and no need to check any of the boxes in the pop up window and then click on the Get Access Token. An n-digit alphanumeric key appears in the text box.
Create a variable access_token and copy the token you just obtained into it.
access_token = 'YOUR ACCESS TOKEN HERE'
graph = facebook.GraphAPI(access_token, version="2.9")The above snippet initiates a graph object with the token that you just created. The version 2.9 is to specify which facebook graph API version you would want to use to scrap the data.
So now that we have the super awesome graph object instatiated, let’s collect all the posts made in a page.
def find_posts(id_or_name, since, until):
posts = graph.get_object('/'+id_or_name+'/'+'posts?fields=message,created_time,id', since=since, until=until,limit=100)
while True:
try:
#convert the obtained json to elastic search format which can be loaded in bulk
write_posts_to_es(posts=posts['data'], index="posts", filename="posts.json")
posts = requests.get(posts['paging']['next']).json()
except KeyError:
# When there are no more pages (['paging']['next']), break fromthe
# loop and end the script.
breakThe above method does two things
-
scrap posts from the page with id or name ‘id_or_name’ from the ‘since’ and until’: If I had to scrap Donald’s posts from 8-Nov-2015 and 8-Nov-2016, I call this method as follows.
find_posts(id_or_name="donaldtrump", since='2015-11-08', until='2016-11-08') -
call a method to store the response obtained in a json file which can uploaded to ES later: As mentioned earlier, we are going to use elastic search for the data analysis and hence we need to save all these posts in a
json filewhich can be uploaded on a single shot to elastic search.
Let’s see what the method write_posts_to_es is all about.
def write_posts_to_es(posts, index, filename):
with open('/Users/jeshocarmel/Documents'+filename,'a') as fp:
for post in posts:
if 'message' in post:
fp.write("""{ "index" : { "_index" : \""""+index+"""\"} }""")
fp.write("\n")
json.dump(post, fp)
fp.write("\n")The above method opens a file and starts writing all the posts that has been scrapped into a file.
Now add main to our script and let it scrap and store
if __name__ == "__main__":
find_posts(id_or_name="donaldtrump", since='2015-11-08', until='2016-11-08')
find_posts(id_or_name="hillaryclinton", since='2015-11-08', until='2016-11-08')Loading data into the super awesome elastic-search
As we have the data now, the next thing we are going to do is to analyse the data. We are going to do find out what is the most spoken term in the candidates posts. Any data analysis requires a proper process and the process always starts with cleaning the data. Then we are going to tokenize the words and then we are going to perform stemming and form a tag cloud of the words. Enough talking, let’s get to business.
cleaning- removal of stopwords such as ‘the’, ‘of’, ‘is’, ‘then’, etctokenize- splitting the sentence into words. e.g. ‘I come from london - ‘I’, ‘come’, ‘from’, ‘london’stemming- A stemming algorithm reduces the words “fishing”, “fished”, and “fisher” to the root word, “fish”
What elastic search does is it performs all of these tasks and much more with just configuring the analyzer=english and setting the fielddata = true. You can follow the links to know what they are as explaining it would be a blog post by itself.
Post this in your kibana dashboard and an index with the name posts is created.
PUT posts
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"message": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english",
"fielddata": true
},
"id":{
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}It’s time to load the data that we have scrapped into elastic search and on a single line command we can load the json file that was created by scrapping into elastic search within a few seconds. Run the following command in command line.
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/x-ndjson" -XPOST localhost:9200/posts/doc/_bulk --data-binary "@posts.json"If everything goes well you will see the data being loaded into elastic search like a pop-up jumping in a windows 97 operating system .

Visualizing with Kibana
Let’s recap what we have done.
- We have scrapped data with python to get all the posts by ‘Trump and Clinton’ 1 year prior to the election date i.e. 08-November-2018 and stored it in a json file.
- We created an index called ‘posts’ in elastic search from Kibana
- We have loaded the json file to elastic-search from command line
Let’s get down to work by opening kibana dashboard. Kibana dashboard usually runs locally on http://localhost:5601/kibana
Kibana offers many visualizations from maps to datatable etc. We are going to use Tag Cloud for our visualization. I’m attaching the config and the tag cloud generated here.
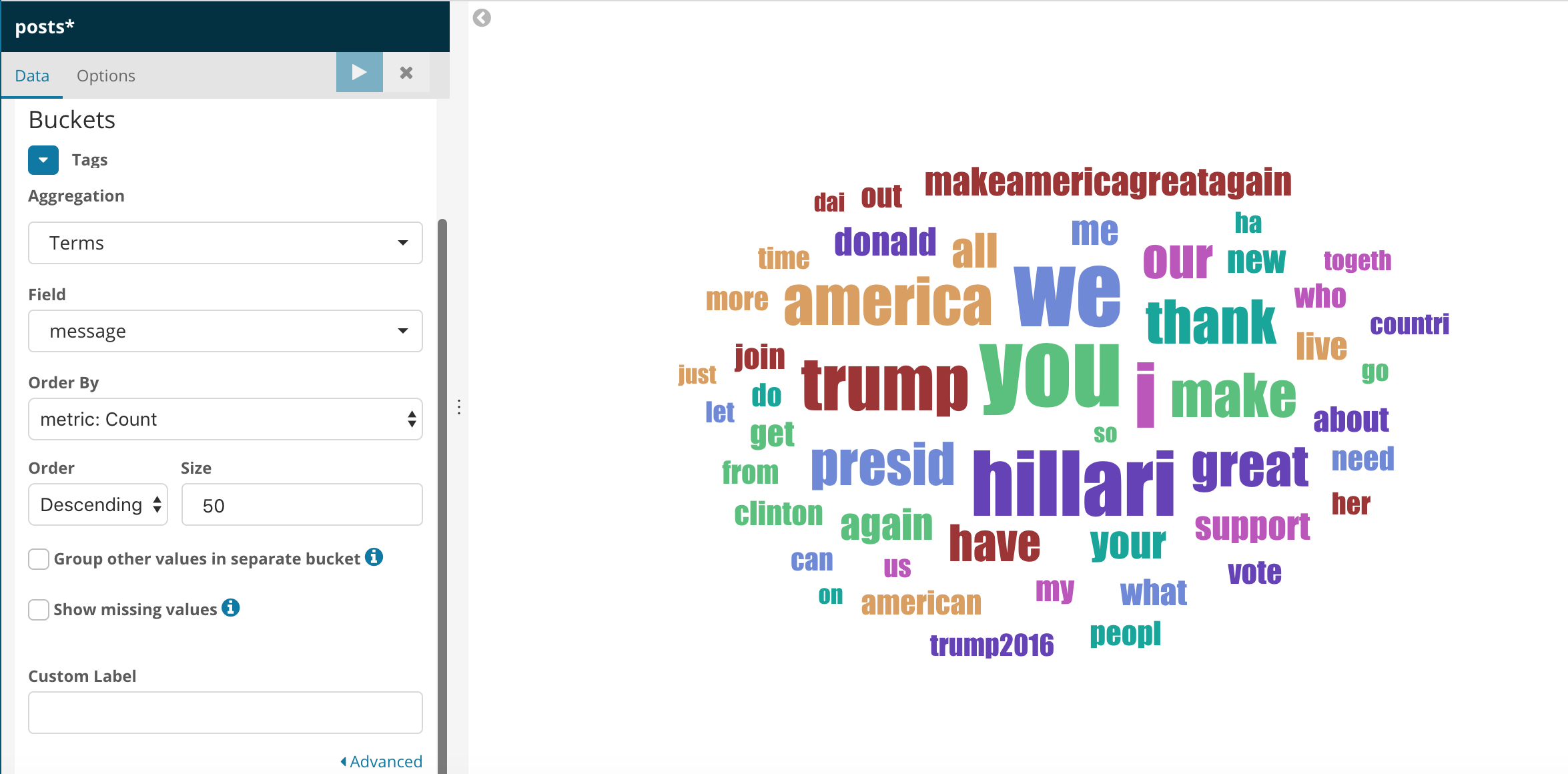
So the words you, we, Hillari, trump has been put forth more by the candidates. If you are wondering why Hillary is pronounced as Hillari, remember stemming which we discussed earlier where fished, fisher get converted to fish? Stemming is one of the key components of natural processing.
Let’s get a bit deep into what is tag cloud by creating the tag cloud’s individually for Donald and Hillary.
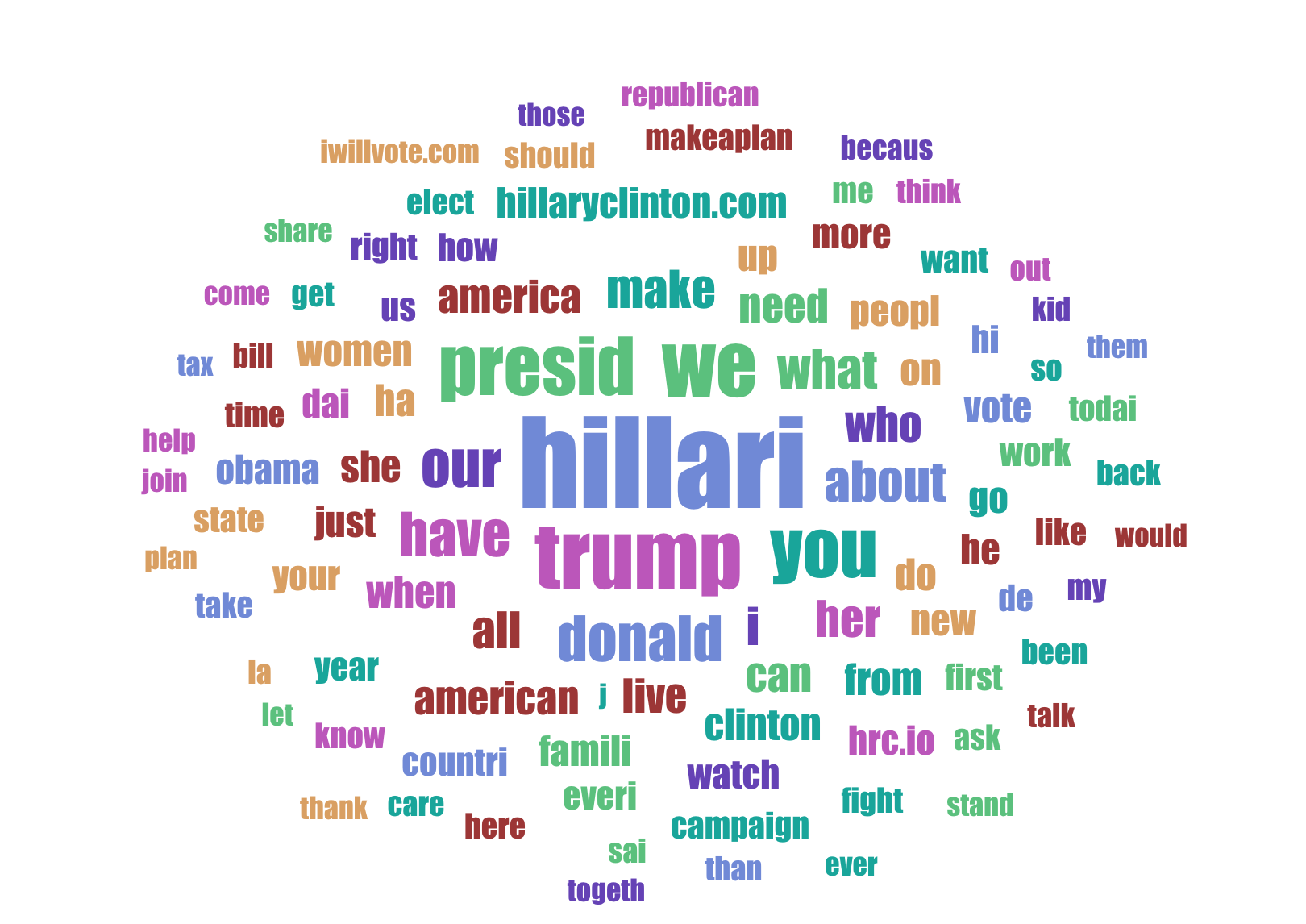 |
|---|
| Tag Cloud for Hillary Clinton’s facebook posts |
Looks like Hillary Clinton was promoting more about her own brand Hillary and also I assume she almost thought she was the president as Presid (after stemming) is one of the most spoken words by her. My personal opinion is that she didn’t give any bigger idea for the american other than the word Hillary Clinton for President.
Let’s see what her rival Donald Trump was upto in the mean time.
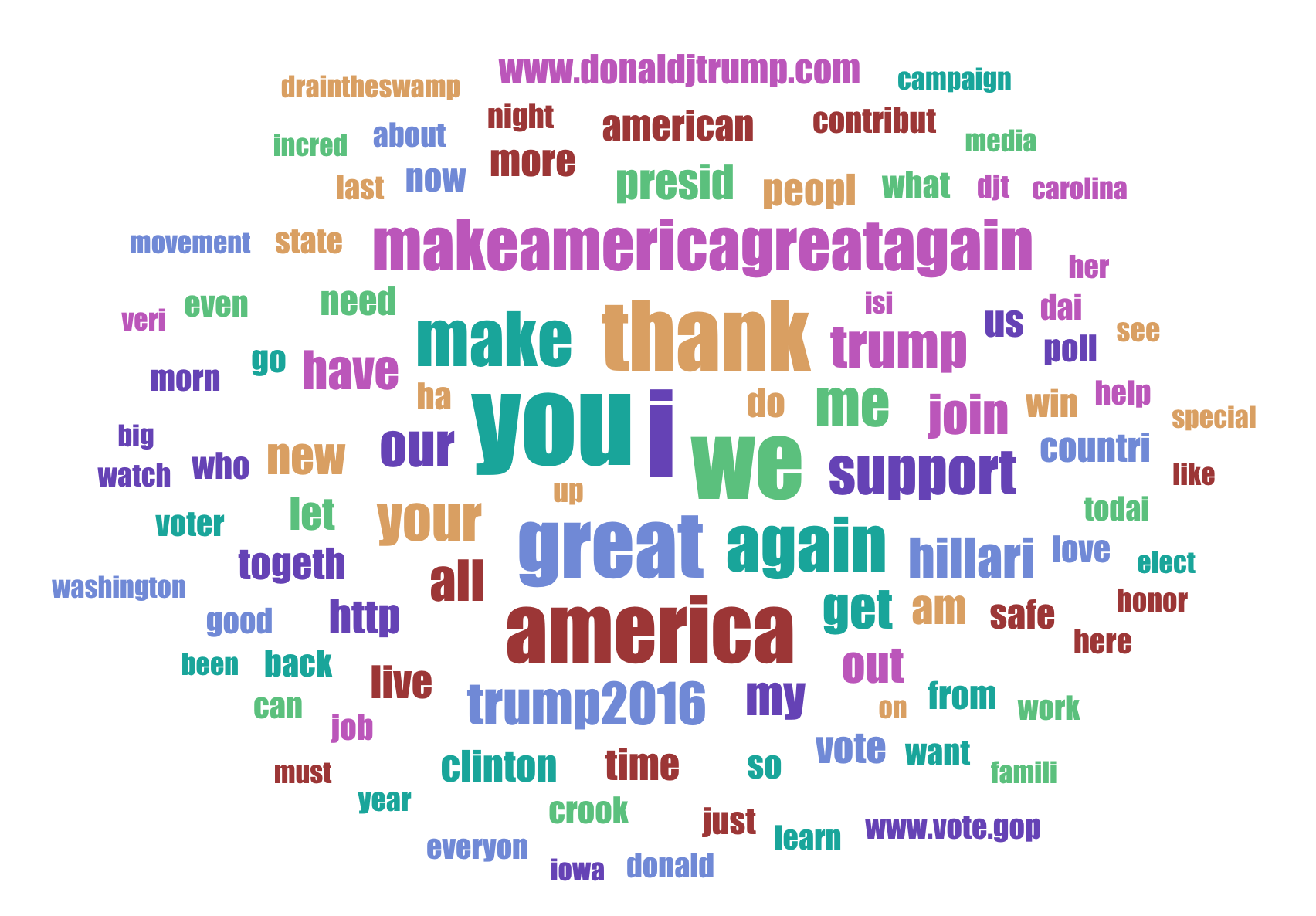 |
|---|
| Tag Cloud for Donald Trump’s facebook posts |
Donald Trump’s main words in his posts were You, We, I, great, America, thank,Me.
Trump was sending a unification message with We, America,You which I believe captured the average Joe’s mind. You can do a deeper analysis into his words and put forth your thesis if you want to but my job here is done.
Thanks folks for reading and I hope you got some insights on scrapping, technology and data analysis. Cheers.